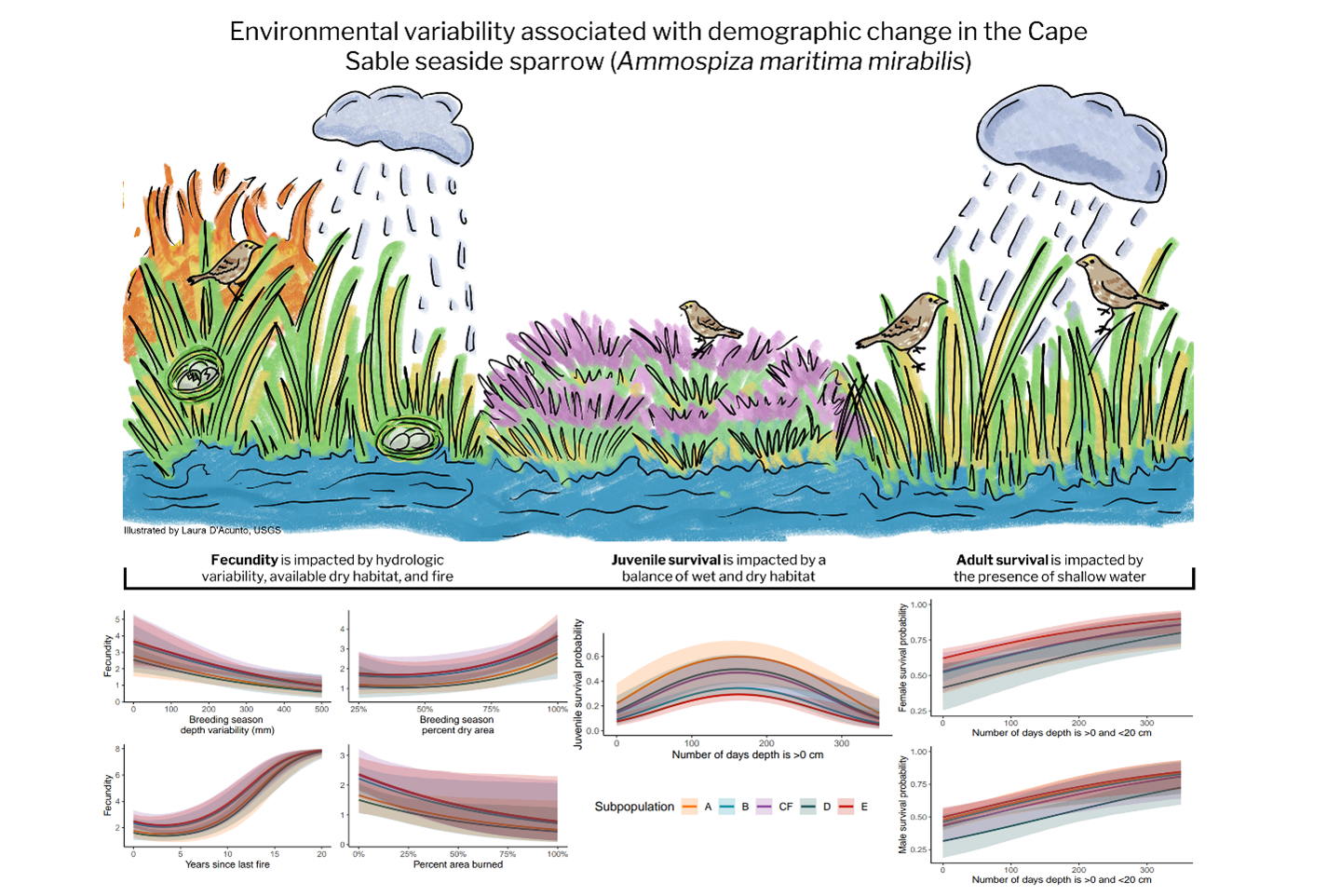
The CSSS IPM-PVA is an integrated population model (IPM) and Bayesian population viability analysis (PVA) of the Cape Sable Seaside Sparrow (CSSS; Ammospiza maritima mirabilis) that provides annual estimates of abundance, apparent survival, fecundity, and growth based on hydrologic and fire conditions from 1992–2021. The IPM-PVA also predicts CSSS extinction risk under simulated environmental conditions with or without sea-level rise.
CSSS IPM-PVA
Martinez, M.T., D'Acunto, L.E., Benscoter, A.M., Haider, S.M., and Romañach, S.S., 2025, Code to fit an integrated population model
and run a population viability analysis for the Cape Sable Seaside Sparrow. U.S. Geological Survey software release,
https://doi.org/10.5066/P1475DJT
Martinez, M.T., D'Acunto, L.E., and Romañach, S.S., 2025, Code to assemble and generate output for an integrated population model of the endangered Cape Sable Seaside Sparrow: U.S. Geological Survey data release, https://doi.org/10.5066/P14PEIAV
Martinez, M.T., D'Acunto, L.E., and Romañach, S.S., 2025, Linking environmental variability to long-term demographic change of an endangered species using integrated population models. Journal of Applied Ecology, https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.70038
Martinez, M.T., D'Acunto, L.E., and Romañach, S.S., 2025, Code to assemble and generate output for an integrated population model of the endangered Cape Sable Seaside Sparrow: U.S. Geological Survey data release, https://doi.org/10.5066/P14PEIAV
Martinez, M.T., D'Acunto, L.E., and Romañach, S.S., 2025, Linking environmental variability to long-term demographic change of an endangered species using integrated population models. Journal of Applied Ecology, https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.70038
Sponsors
